Tri par sélection en java
Nous pouvons créer un programme Java pour trier les éléments d’un tableau à l’aide du tri par sélection. Dans l’algorithme de tri par sélection, nous cherchons l’élément le plus petit et on le met au bon endroit. Nous échangeons l’élément en cours avec le prochain élément le plus petit.
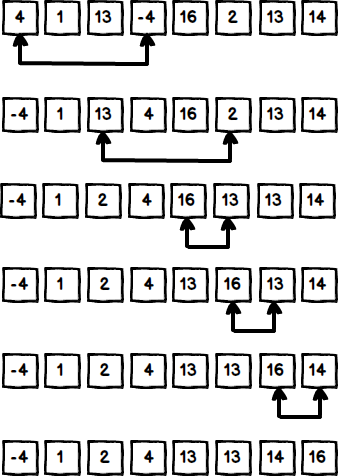
Exemple de Tri par sélection en Java
public class AlgoTriParSelection {
public static void tri_selection(int[] tab)
{
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length - 1; i++)
{
int index = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < tab.length; j++)
{
if (tab[j] < tab[index]){
index = j;
}
}
int min = tab[index];
tab[index] = tab[i];
tab[i] = min;
}
}
static void displayTab(int[] tab){
for(int i=0; i < tab.length; i++)
{
System.out.print(tab[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String a[])
{
int[] tab = {-4, 1, 13, 4, 16, 2, 13, 14};
System.out.println("**** Avant le tri par selection *****");
displayTab(tab);
//tri d un tableau avec l algorithme de tri par selection
tri_selection(tab);
System.out.println("**** Apres le tri par selection ****");
displayTab(tab);
}
}
La sortie
**** Avant le tri par selection ***** -4 1 13 4 16 2 13 14 **** Apres le tri par selection **** -4 1 2 4 13 13 14 16
La complexité temporelle du tri par selection
Meilleur: Θ(n2)
Moyenne: Θ(n2)
Pire: O(n2)
La complexité spatiale du tri par selection
O(1)







